The Internet has come far since 1983, and it’s entirely different from its early beginnings. Web usage has exploded in relevance as years go by, and the traffic surge has grown nearly tenfold yearly. With the high traffic surge, a main crisis set to rise is a lack of speed. When a consumer is trying to visit your store from the other side of the world, sometimes a common problem that any customer could face is the time for the content to appear on the screen. Now this could take a while longer than you expect. A primary reason for this can be web hosting, reduced bandwidth, and much more. A probable solution to tackle this problem is to invest in Content Delivery Network.
Now if you are a business owner or a tech-savvy developer, it’s crucial to understand CDNs. Well, this is essential to optimize your online presence. We live in the epicenter of growing technology, and we can’t blame consumers for needing the best they can get their hands on. So I have put out this beginner’s guide so you can know what, why, and how they are essential for your business.
What is CDN – A hypothetical definition
A CDN or Content Delivery Network is a global distribution of an interconnecting network of servers designed to work together to provide faster transfer of assets required for loading content on your website, like HTML pages, images, videos, etc.
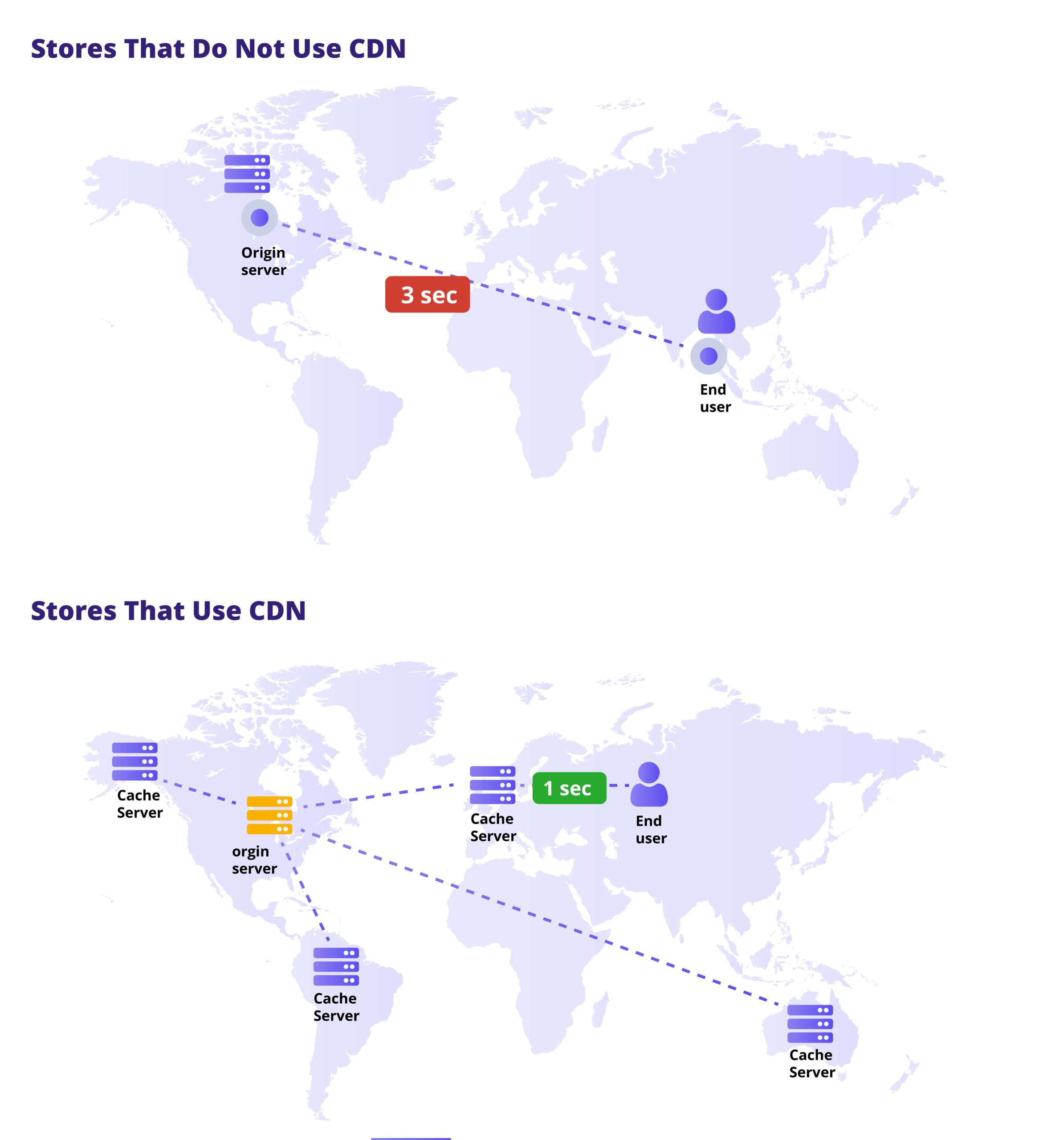
Content Delivery Network has a number of intermediate servers that are strategically located data centers that store cached data and delivers when needed. This works with the goal of reducing the physical distance between the store’s actual server and the customer.
Understanding Content Delivery Network- Let’s analyze a simple case.
So imagine being a store owner based in Sweden and a customer based in Japan looking to buy something from your store. Here the CDN would work from an edge server based in Japan. The proxy server based in Japan, which is physically closer to the user, would deliver the content to the user right away. This is much easier and more efficient than waiting for the actual server to deliver the content, which might take long.
The first generation CDNs came into existence in the late 90s. Even though there have been several technological advancements preceding them, from server farms and hierarchical caching to caching proxy development, all these have set the foundation for bringing the first CDN ever.
First, Second and Third Generation CDNs
First Generation or Static CDN released in 1997
First-generation CDNs were developed for HTML and downloadable files. They could optimize stores and even support expanding content volumes. Other than that, they aimed to let companies provide products and services to effectively handle customer requests without a considerable revenue loss while managing their IT infrastructure.
Second Generation or Dynamic CDN released in 2001
While the second generation gave greater importance on peer to peer production and energy awareness, it also served both as static and dynamic content and cloud computing to meet the growing demand for interactivity set forward by all devices. This generation also paved the path for delivering content to mobile device users with the usage of P2P and cloud computing techniques. ISPs, tech companies, telcos, and broadcasters set foot into the CDN industry during the second generation, with few of them even becoming significant players in the Industry.
Third Generation or Multi-Purpose CDN released in 2010
Currently, third-generation CDNs are still evolving and growing with new research and development. Multi-Purpose CDN serves both dynamic and static content, including rich media. So do look out for CDNs that increasingly support future generations. The envision for the third-generation CDNs is that they should be autonomous, community-driven, and self-manageable. So giving an autonomic content delivery ensure that the quality of user experience is on the next level.
Why are CDNs Important?
Usually, Content Delivery Networks are for loading pages quickly. However, they can also de-clutter the local network and directs through busy server networks for load balancing, with the ultimate goal of eliminating the risk of a single point of server failure.
CDNs usually play an important role in load balancing. Imagine a website experiencing a sudden high traffic surge during sales. So in order to meet multiple requests across different servers and prevent overloading one server, you can rely on CDNs.
Another important and handy aspect of CDNs is that it has improved availability. Well, even if your actual server crashes due to traffic or any other reason, CDNs usually maintain continuous service by providing cached content from the nearest available edge servers.
Lastly, CDNs contribute to improving store security. Content Delivery Networks have the capability to manage your site during traffic surges. It is highly resilient against security threats like DDoS attacks.
Content Delivery Networks also provide protection for stores through the Web Application Firewall (WAF). WAF thoroughly analyses website traffic examines each HTTP request, and blocks suspicious activities. This effectively helps to safeguard your store against threats like SQL injection or Cross-site Scripting attacks.
Types of Content Delivery Network
Now CDNs might not be extremely important to visitors, as half of the visitors are not aware of what a Content Delivery Network is. Even though what type might not matter to them, certain aspects, like performance, security adaptability, and reliability, matter to the consumers. While for the Store owner, it is wise that you check on what types of CDNs are out there.
P2P Content Delivery Network
Peer to Peer Content Delivery Network utilizes the Peer to Peer (P2P) protocol. µTorrent users might recognize this protocol. So how P2P works is that the system is designed to provide anonymized routing of network traffic giving massive parallel computing environments, distributed storage, and other functions. Other than µTorrent, P2P Content Delivery Networks are used by several NGOs and big and middle corporations. In a P2P content delivery network, the end-users are also part of the Delivery Network, so they concurrently upload web content components while downloading or accessing live streaming. Another aspect is that no caching is involved in peer-to-peer content delivery networks. Since they require low resources and hardware, several CDN providers in the market offer P2P services like PPS, PeerCast, and Freecast.
Push CDN
Push CDN is the content delivery network type, where the actual servers would directly send web content to CDN servers. A simpler way to explain this is that the CDNs server somewhat acts similarly to how the original server acts.
A likely scenario is that the origin server would directly feed the contents to the CDN server either manually or automatically, which is later integrated into it. So these pushed contents are cached in the server unless the webmaster purges or deletes them. The main catch here is that the webmaster is liable for the content sent to the CDN, which you consumers will later see in your store. As the CDN receives a request, the content that is required is “pushed” from the CDN and redirected to the customers.
Pull CDN
Now Pull CDN is the complete opposite of Push CDN. Here, the CDN is tasked with “Pulling” the web content that is served to customers once their request is received. The site owner can let the content stay on the origin servers, but the URLs are rewritten so that they direct to the CDN servers and remain there until they expire. Pull CDN, or Relayed CDN, is a highly recommended CDN for WordPress sites.
Are CDN and Web Hosting the same?
First things first, Content Delivery Network does not host content, or it cannot replace the actual web hosting. What it does is it caches the content at the network edge so that it can improve website performance. While a traditional web hosting server is developed to occupy all your website content assets. With CDN caching, you can access the adjacent edge servers set around the globe with your store’s cached content. In recent years CDN has gained quite a popularity, as they could effectively address the primary issues set forward by traditional web hosting by setting caching, reducing hosting bandwidth, helping to prevent service interruptions, and enhancing security.
So does your store require Content Delivery Network?
So for starters, implementing CDNs is ideal for businesses with a global or wider audience, high traffic, or stores that heavily rely on media content like images, videos, or larger files. With the right CDN choice, you can optimize your content delivery, reduce bandwidth usage, and improve your store.
But if you are a small business owner that operates in one location and works across a small geographical area, do note that opting for a CDN is not very beneficial for your business unless you are looking forward to expanding to a wider audience. In certain scenarios, introducing CDNs is not a great idea, especially if you are a small store, as the unnecessary introduction of another point of connection between visitors and your origin or nearby server might worsen your website performance.
Finally, opting for a CDN that works for your store totally relies on your specific needs, your budget, and other technical requirements.
CDNs work best for large-scale businesses.
- If you are a global store owner or expanding your e-commerce business worldwide, integrating it is beneficial as it can handle the heavy traffic coming from all over the world to your site.
- The advertising business uses heavy multimedia-based ads for engagement and to attract audiences, for them, it is ideal as they need more resources to load the content properly and on time.
- Online Gaming Industry is the leading user of CDNs, as they need more resources so as to deliver to give the best gaming experience for the users.
- Finally, the entertainment industry and OTT platforms are in need to use CDN as they require to live streaming and downloading options for users all over the world.
Does using a Content Delivery Network affect your SEO?
Figuring out CDN can be quite overwhelming, as the concept surrounding it can be vast and extensive. When it comes to CDNs, there are a lot of misinterpretations, and one of that is, does using CDN affect SEO?
In general, CDNs don’t have any real effect on your store ranking, but they do have the ability to improve your store’s performance. Now this can effectively enhance the loading speed, potentially reflecting on giving your customers a great user experience and improving Core Web Vitals scores. The main advantage of hosting images on the same domain is that it can simplify the process of switching to CDNs.
Now the other myth you might have come across is that hosting images on a CDN domain, rather than a website domain, can eventually have an adverse impact on your website ranking in organic search results.
Well, this was busted long ago by Google representatives. If you use the same domain to host your image, content makes zero difference SEO-wise and would not have an impact on how the image is ranked.
How does a CDN improve page load time?
CDNs have many indirect advantages besides just giving better store performance through high traffic. It also gives highly enhanced security, making your system less vulnerable to attacks, including DNS attacks. But the biggest advantage of all is that they speed up your site. Content delivery network often leverages the geographical proximity of the servers across various locations to improve performance metrics like page load time and latency.
Here is how CDN (Content Delivery Network) can improve page load time:
Reduced latency
Content delivery networks often have distributed servers across multiple geographic locations. Well, this often makes it easy when a visitor request content from your site, and the CDN can serve the content from the nearest to the user’s locations. With this, the distance required for the data to travel will become short, resulting in lower latency and quicker content delivery.
Caching
CDNs often contain cached content of your store’s static content on their servers, making it easier for the CDN to deliver the content directly from the cache it formerly saved when the customer requested it rather than going all the way to the origin server and fetching it. Caching makes retrieving user requests and delivering content effortless while improving page load speed.
Load distribution
Offloading content delivery to several CDN servers is an optimal way to reduce the load on your origin server. Distributing your content across multiple CDNs can help maintain faster response times and improve your site’s overall performance. Load distribution will aid the origin server in concentrating on handling dynamic requests, which is more important to keep your store on the float.
Parallelized downloads
It is quite normal for CDNs to split the content into smaller components. This is to download them continuously from multiple CDN servers. By parallelized downloading, you can easily leverage the browser’s ability to handle several connections simultaneously. Furthermore, this reduces the page load time.
Global network
Now this is not something new, the CDNs have a wide presence across the world. So despite the customer’s geographical location. The CDNs can access content from the nearest CDN server so as to reduce network congestion and boost the site’s overall performance.
How to Choose a CDN Provider?

Now while choosing a CDN provider, there are various factors you should consider. The technology and feature set of each CDN provider offer can differ, and some of these features set them apart. There are CDN providers in the market that offer free services and while others offer both free and premium services. A main factor that plays while choosing is to pick a service that could meet your store’s requirements and budget.
Here are some of the key sets of features to look out for.
- The store owner should decide on which kind of caching method would work best for your store, So it’s vital to pick a provider that offers Push or Pull functionality.
- Origin shield is a feature that works as an additional caching mechanism between an origin server and a CDN edge server. With Origin Shield, you can reduce the workload on the primary server.
- So the CDN providers should have Logging features that let the users search, analyze, store, and surveil the logging data and events.
- Make sure it has Cache-control, the HTTP cache header sanctions the user to decide how or when a store’s resources can cache along with when the cached content expires. Picking up a CDN service that lets you customize and personalize a CDN that suits your website requirements. Certain CDN providers sometimes allow the user access to modify their asset delivery, security measures, etc.
- Even though CDN can hide the origin server’s IP address, there is still a need for an extra layer of security to deviate from network layer attacks and provide robust security to protect the store from potential cyber threats.
- The CDN must support HTTP/2, as it is reliable and quite secure compared to regular HTTP protocol, and it has better and faster performance.
- It should have diagnostic, analytics, and reporting tools to monitor the server’s overall health and optimize CDN configuration.
- Should have geo-filtering so as to direct paths on your CDN endpoint and also decide the rules to restrain certain web content based on the locations.
Well, a few content delivery networks are well-known among users, and you should definitely check out Cloudflare, Keycdn.com, bunny.net or rackspace.
And a Final Note,
With more online stores popping in every single day, the use of the Internet is increasing day by day. CDNs have become an essential cornerstone for your store if you are looking forward to expanding your audience globally and reaching potential customers worldwide. You wanna keep your customers to keep on coming for more, like a moth to a flame, and drag them in with faster loading time and highly improved user experience. Be it products, services, or information, give the users what they need with a dash of good user experience and reduce page load speed which can be done by opting for a Good CDN.









 THANK YOU!
THANK YOU!